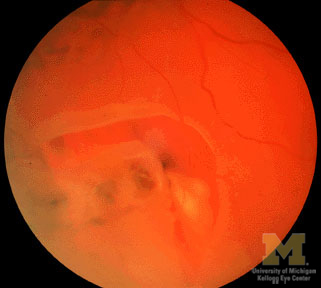
Retinal Break
- Hole in neurosensory part of retina causes it to separate from underlying retinal pigment epithelium
- Usually results from tugging by vitreous
- Common causes are eye trauma (including intraocular surgery), high myopia, intraocular inflammation, diabetes, and aging
- Can lead to retinal detachment
- May be asymptomatic, or...
- Patient reports sudden onset of flashes and/or floaters
- Hole in retinal periphery usually not seen with direct ophthalmoscopy and even hard to detect with indirect ophthalmoscopy
- Vitreous tug on retina without retinal break
- Vitreous separation from retina without retinal break
- Refer urgently patient with new-onset flashes or floaters
- Retinal break may need to be repaired to prevent retinal detachment