Cataract
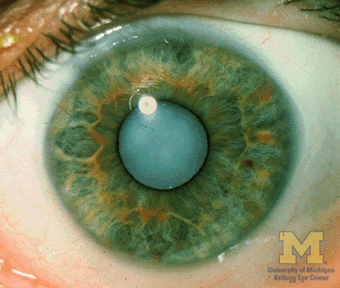
- Opacification of eye’s crystalline lens
- Called "cataract" by Greek physicians who thought it looked like a waterfall
- Caused by aging degeneration of lens protein
- Also caused by intraocular inflammation, trauma, metabolic and hereditary disorders
- Patient reports slowly progressive blurred vision in affected eye
- Vision often improves with pinhole
- Early cataract visible with slit lamp biomicroscope as golden, gray, black discoloration of lens
- Advanced cataract visible with ophthalmoscope as loss of "red reflex" in pupil
- Uncorrected refractive error, corneal, retinal, and visual pathway lesions
- Dense cataracts, which make pupil look gray or white, are mimicked by vitreous and retinal lesions
- Cataracts are removed surgically through small incisions and ultrasonic fragmentation
- Posterior lens capsule left behind
- Plastic lens implant inserted in place of extracted crystalline lens
- Surgical procedure takes less than 30 minutes and is painless
- Visual recovery prompt and full in 99% of eyes provided no other reason for subnormal sight
- Posterior lens capsule remnant may opacify and require laser treatment
