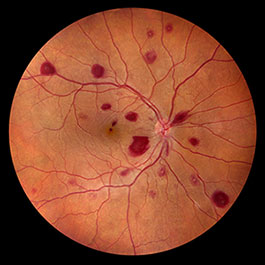
Leukemia
- Neoplastic proliferation of white blood cells
- Four main types: acute and chronic myelogenous, acute and chronic lymphogenous
- Systemic manifestations include fever, fatigue, bleeding, lymph node and spleen enlargement
- Diagnosis based on blood count, blood smear, and bone marrow pathology
- Most common ophthalmic manifestation: retinal hemorrhages
- Retinal hemorrhages
- Occur when platelet count drops to 20,000 or below
- Retinal artery or vein occlusions occur if total leukocyte count is 100,000 or above
- Other blood dyscrasias
- Diabetes mellitus, but more hard exudates
- Systemic hypertension, connective tissue disorders, vasculitis
- Refer urgently any patient with new vision loss and known leukemia or other blood dyscrasia
- Retinal changes will resolve spontaneously if blood counts improve
- White cell counts above 100,000 can lead to slowed blood flow ("leukostasis") and occlusion of large retinal vessels with permanent vision loss