Deferoxamine
Medication that binds iron and treats iron overload occurring after frequent blood transfusions Most common ophthalmic side effect: damage to retinal pigment epithelium, photoreceptors, retinal ganglion cells
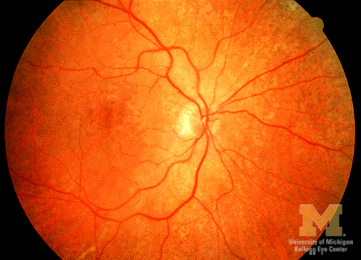
Patient complains of impaired visual acuity, visual field, night vision, color vision Symptoms develop after acute or chronic administration of deferoxamine Ophthalmoscopy normal at symptom onset Ophthalmoscopy later shows fine retinal speckled pigmentation or pale optic discs Once ophthalmoscopic signs have appeared, visual dysfunction may be irreversible even if medication stopped Electroretinography detects abnormalities before ophthalmoscopy
Refer patients for baseline ophthalmological examination before starting medication Refer for reexamination every three months while on treatment Refer promptly for reexamination if patient develops visual symptoms
If toxicity diagnosed early, visual loss may be reversible or non-disabling Medication must be stopped at diagnosis of ocular toxicity and later resumed at lower dose or replaced with alternative iron chelator, depending on visual manifestations