Topiramate
- Medication used to treat seizures and migraine
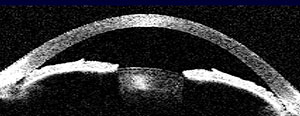
- Most common ophthalmic side effect: angle-closure glaucoma caused by edema of the ciliary body
- Incidence of this side effect estimated at 2%
- Avoid prescribing topiramate if ophthalmologist has documented that patient has narrow anterior chamber angle
- Refer emergently to ophthalmologist any patient with acute eye pain or visual symptoms who is taking topiramate
- Discontinue topiramate if angle closure glaucoma is confirmed
- Intraocular pressure must be lowered promptly with aqueous suppressants, cycloplegia, topical corticosteroids
- Peripheral iridectomy, standard approach to angle closure glaucoma not caused by topiramate, does not work here
- Permanent vision loss has resulted from angle closure precipitated by topiramate even when diagnosis and treatment are undertaken promptly