Minocycline
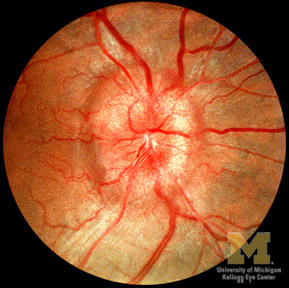
Antibiotic derived from tetracycline used against wide variety of bacteria Treats refractory acne vulgaris Most common ophthalmic side effect: papilledema (from increased intracranial pressure)
Headache, neck pain, transient or persistent loss of vision, and... Loss of vision even WITHOUT headache or other symptoms Symptoms begin within weeks to months after starting standard doses of minocycline Swollen optic discs (papilledema ) Visual fields abnormal, reflecting axonal damage from chronically elevated intracranial pressure Brain imaging normal Lumbar puncture discloses high opening pressure and normal cerebrospinal constituents
Isotretinoin-induced increased intracranial pressure Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) Brain tumor Meningitis Hydrocephalus Optic neuritis Ischemic optic neuropathy in giant cell arteritis Compressive or infiltrative optic neuropathy from cancer
Refer promptly to ophthalmologist any patient with visual symptoms and/or headache who is using minocycline Consider baseline ophthalmologic screening and routine screening every 3-6 months because papilledema can exist at first without causing visual symptoms
Vision loss may be delayed because axonal damage in papilledema proceeds slowly and initially spares visual acuity Vision loss reversible if papilledema detected early Vision loss permanent and disabling if papilledema detected late